A collaborative work between members of the Multifunctional Optical Materials and Surface Nanotechnology groups, both at ICMS, has been featured in the ACS Editors’ Choice section on July 9.
Through the ACS Editors’ Choice distinction, the American Chemical Society publisher highlights the special relevance of recently published works. This selection is made based on the recommendations of more than 400 editors of the publisher’s 44 journals. In this way, the selected publications are offered to the general public through free access because they are considered of great interest to the international scientific community. The ACS Editors’ Choice distinction exemplifies the publisher’s commitment to improving the quality of people’s lives through the transformative power of chemistry.
About the selected article
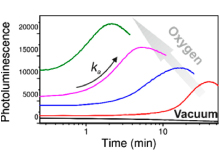
The article selected as ACS Editors’ Choice postulates and demonstrates a mechanism that explains the changes in the photoluminescence of metal-halide hybrid perovskites in the presence of oxygen. This family of perovskites has gained great relevance in recent years due to their optoelectronic properties, which, together with the easy manufacturing processes they require, make them serious candidates for implementation in solar cells and lighting devices. However, their limited stability under lighting or in the presence of various environments is slowing down the adoption of these materials by the industry.
In the work recognized here, the authors have experimentally demonstrated that the activation and deactivation of light emission in these perovskites is related to ionic migration promoted by the formation of reduced oxygen species on the surface of the material. This has been possible thanks to a novel combination of characterization techniques that has allowed the analysis of the photoluminescence of the material while monitoring chemical changes on its surface through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Although the emission behavior of these perovskites was known, until now there was no precise explanation of the photochemistry and photophysics inherent to the process. This work represents a step forward in the understanding of the emission phenomena of these semiconductors in the presence of different atmospheric conditions. Thanks to this research, new strategies are opened to improve the stability and performance of solar devices and LEDs eventually manufactured from hybrid metal-halide perovskites.
The results are collected in the article with reference: Miguel Anaya, Juan F. Galisteo-López, Mauricio E. Calvo, Juan P. Espinós and Hernán Míguez. Origin of Light-Induced Photophysical Effects in Organic Metal Halide Perovskites in the Presence of Oxygen. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 2018, 9, 3891, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b01830.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b01830
ICMS Intergroup Collaboration Named ACS Editors’ Choice®